- [email protected]
- 27-31 Wright St, Clayton VIC 3168
- Contact
08Jun
Breathing matters – Nature Reviews Neuroscience
by Elazadeh, 0 Comments

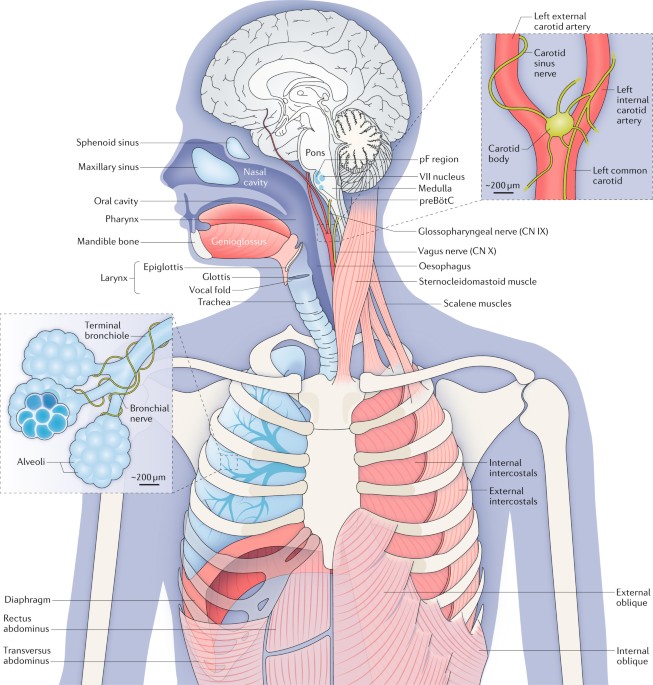
-
Smith, J. C., Ellenberger, H. H., Ballanyi, K., Richter, D. W. & Feldman, J. L. Pre-Bötzinger complex: a brainstem region that may generate respiratory rhythm in mammals. Science 254, 726–729 (1991). This seminal work announced the preBötC, which was identified and named in reference 15 cited therein.
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Schwarzacher, S. W., Smith, J. C. & Richter, D. W. Pre-Bötzinger complex in the cat. J. Neurophysiol. 73, 1452–1461 (1995).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Schwarzacher, S. W., Rüb, U. & Deller, T. Neuroanatomical characteristics of the human pre-Bötzinger Complex and its involvement in neurodegenerative brainstem diseases. Brain J. Neurol. 134, 24–35 (2011).
Article
Google Scholar
-
Tupal, S. et al. Testing the role of preBötzinger complex somatostatin neurons in respiratory and vocal behaviors. Eur. J. Neurosci. 40, 3067–3077 (2014).
PubMed
PubMed Central
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Wenninger, J. M. et al. Large lesions in the pre-Bötzinger complex area eliminate eupneic respiratory rhythm in awake goats. J. Appl. Physiol. 97, 1629–1636 (2004).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Pantaleo, T., Mutolo, D., Cinelli, E. & Bongianni, F. Respiratory responses to somatostatin microinjections into the Bötzinger complex and the pre-Bötzinger complex of the rabbit. Neurosci. Lett. 498, 26–30 (2011).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Bongianni, F., Mutolo, D., Cinelli, E. & Pantaleo, T. Respiratory responses induced by blockades of GABA and glycine receptors within the Bötzinger complex and the pre-Bötzinger complex of the rabbit. Brain Res. 1344, 134–147 (2010).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Smith, J. C., Morrison, D. E., Ellenberger, H. H., Otto, M. R. & Feldman, J. L. Brainstem projections to the major respiratory neuron populations in the medulla of the cat. J. Comp. Neurol. 281, 69–96 (1989).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Dobbins, E. G. & Feldman, J. L. Brainstem network controlling descending drive to phrenic motoneurons in rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 347, 64–86 (1994).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Wu, J. et al. A V0 core neuronal circuit for inspiration. Nat. Commun. 8, 544 (2017).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Tan, W., Pagliardini, S., Yang, P., Janczewski, W. A. & Feldman, J. L. Projections of preBötzinger Complex neurons in adult rats. J. Comp. Neurol. 518, 1862–1878 (2010).
PubMed
PubMed Central
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Yackle, K. et al. Breathing control center neurons that promote arousal in mice. Science 355, 1411–1415 (2017).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Yang, C. & Feldman, J. Efferent projections of excitatory and inhibitory preBötzinger Complex neurons. J. Comp. Neurol. 526, 1389–1402 (2018).
-
Funk, G. D., Smith, J. C. & Feldman, J. L. Generation and transmission of respiratory oscillations in medullary slices: role of excitatory amino acids. J. Neurophysiol. 70, 1497–1515 (1993).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Johnson, S. M., Smith, J. C. & Feldman, J. L. Modulation of respiratory rhythm in vitro: role of Gi/o protein-mediated mechanisms. J. Appl. Physiol. 80, 2120–2133 (1996).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Gray, P. A., Rekling, J. C., Bocchiaro, C. M. & Feldman, J. L. Modulation of respiratory frequency by peptidergic input to rhythmogenic neurons in the preBötzinger Complex. Science 286, 1566–1568 (1999). This report demonstrates that neuropeptide receptor expression characterizes constituent preBötC rhythmogenic neurons and demarcates the borders of the preBötC.
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Stornetta, R. L. et al. A group of glutamatergic interneurons expressing high levels of both neurokinin-1 receptors and somatostatin identifies the region of the pre-Bötzinger Complex. J. Comp. Neurol. 455, 499–512 (2003).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Wang, H., Stornetta, R. L., Rosin, D. L. & Guyenet, P. G. Neurokinin-1 receptor-immunoreactive neurons of the ventral respiratory group in the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 434, 128–146 (2001).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Guyenet, P. G. & Wang, H. Pre-Bötzinger neurons with preinspiratory discharges ‘in vivo’ express NK1 receptors in the rat. J. Neurophysiol. 86, 438–446 (2001).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Hayes, J. A. & Del Negro, C. A. Neurokinin receptor-expressing pre-Bötzinger complex neurons in neonatal mice studied in vitro. J. Neurophysiol. 97, 4215–4224 (2007).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Liu, Y.-Y. et al. Substance P and enkephalinergic synapses onto neurokinin-1 receptor-immunoreactive neurons in the pre-Bötzinger complex of rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 19, 65–75 (2004).
PubMed
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Peña, F. & Ramirez, J.-M. Substance P-mediated modulation of pacemaker properties in the mammalian respiratory network. J. Neurosci. 24, 7549–7556 (2004).
PubMed
Article
CAS
PubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
-
Ramírez-Jarquín, J. O. et al. Somatostatin modulates generation of inspiratory rhythms and determines asphyxia survival. Peptides 34, 360–372 (2012).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Llona, I. & Eugenín, J. Central actions of somatostatin in the generation and control of breathing. Biol. Res. 38, 347–352 (2005).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Rekling, J. C., Champagnat, J. & Denavit-Saubié, M. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) depolarizes a subset of inspiratory neurons in the newborn mouse brain stem in vitro. J. Neurophysiol. 75, 811–819 (1996).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Gray, P. A., Janczewski, W. A., Mellen, N., McCrimmon, D. R. & Feldman, J. L. Normal breathing requires preBötzinger complex neurokinin-1 receptor-expressing neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 4, 927–930 (2001).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
McKay, L. C., Janczewski, W. A. & Feldman, J. L. Sleep-disordered breathing after targeted ablation of preBötzinger complex neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 8, 1142–1144 (2005).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Wenninger, J. M. et al. Small reduction of neurokinin-1 receptor-expressing neurons in the pre-Bötzinger complex area induces abnormal breathing periods in awake goats. J. Appl. Physiol. 97, 1620–1628 (2004).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Tan, W. et al. Silencing preBötzinger Complex somatostatin-expressing neurons induces persistent apnea in awake rat. Nat. Neurosci. 11, 538–540 (2008).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Stornetta, R. L., Sevigny, C. P. & Guyenet, P. G. Inspiratory augmenting bulbospinal neurons express both glutamatergic and enkephalinergic phenotypes. J. Comp. Neurol. 455, 113–124 (2003).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Guyenet, P. G., Sevigny, C. P., Weston, M. C. & Stornetta, R. L. Neurokinin-1 receptor-expressing cells of the ventral respiratory group are functionally heterogeneous and predominantly glutamatergic. J. Neurosci. 22, 3806–3816 (2002).
PubMed
Article
CAS
PubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
-
Coveñas, R. et al. Mapping of neurokinin-like immunoreactivity in the human brainstem. BMC Neurosci. 4, 3 (2003).
PubMed
PubMed Central
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Liu, Y. Y., Ju, G. & Wong-Riley, M. T. Distribution and colocalization of neurotransmitters and receptors in the pre-Bötzinger complex of rats. J. Appl. Physiol. 91, 1387–1395 (2001).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Fukuda, H., Nakamura, E., Koga, T., Furukawa, N. & Shiroshita, Y. The site of the anti-emetic action of tachykinin NK1 receptor antagonists may exist in the medullary area adjacent to the semicompact part of the nucleus ambiguus. Brain Res. 818, 439–449 (1999).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Nakaya, Y., Kaneko, T., Shigemoto, R., Nakanishi, S. & Mizuno, N. Immunohistochemical localization of substance P receptor in the central nervous system of the adult rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 347, 249–274 (1994).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Yamamoto, Y., Onimaru, H. & Homma, I. Effect of substance P on respiratory rhythm and pre-inspiratory neurons in the ventrolateral structure of rostral medulla oblongata: an in vitro study. Brain Res. 599, 272–276 (1992).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Le Gal, J.-P., Juvin, L., Cardoit, L., Thoby-Brisson, M. & Morin, D. Remote control of respiratory neural network by spinal locomotor generators. PLOS ONE 9, e89670 (2014).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Tan, W. et al. Reelin demarcates a subset of pre-Bötzinger complex neurons in adult rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 520, 606–619 (2012).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Cui, Y. et al. Defining preBötzinger Complex rhythm- and pattern-generating neural microcircuits in vivo. Neuron 91, 602–614 (2016).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Koizumi, H. et al. Voltage-dependent rhythmogenic property of respiratory pre-Bötzinger complex glutamatergic, Dbx1-derived, and somatostatin-expressing neuron populations revealed by graded optogenetic inhibition. eNeuro https://doi.org/10.1523/eneuro.0081-16.2016 (2016).
-
Moore, J. D. et al. Hierarchy of orofacial rhythms revealed through whisking and breathing. Nature 497, 205–210 (2013). This work shows that preBötC-driven inspiratory rhythms act as a master oscillator for orofacial behaviours.
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Moore, J. D., Kleinfeld, D. & Wang, F. How the brainstem controls orofacial behaviors comprised of rhythmic actions. Trends Neurosci. 37, 370–380 (2014).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Kottick, A., Martin, C. A. & Del Negro, C. A. Fate mapping neurons and glia derived from Dbx1-expressing progenitors in mouse preBötzinger complex. Physiol. Rep. 5, e13300 (2017).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Bouvier, J. et al. Hindbrain interneurons and axon guidance signaling critical for breathing. Nat. Neurosci. 13, 1066–1074 (2010).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Gray, P. A. et al. Developmental origin of preBötzinger Complex respiratory neurons. J. Neurosci. 30, 14883–14895 (2010). This work, in conjunction with Ref. 44, shows that rhythmogenic preBötC neurons in perinatal mice are derived from DBX1-expressing precursors.
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Picardo, M. C. D., Weragalaarachchi, K. T. H., Akins, V. T. & Del Negro, C. A. Physiological and morphological properties of Dbx1-derived respiratory neurons in the pre-Bötzinger complex of neonatal mice. J. Physiol. 591, 2687–2703 (2013).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Vann, N. C., Pham, F. D., Hayes, J. A., Kottick, A. & Del Negro, C. A. Transient suppression of Dbx1 preBötzinger interneurons disrupts breathing in adult mice. PLOS ONE 11, e0162418 (2016).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Wang, X. et al. Laser ablation of Dbx1 neurons in the pre-Bötzinger complex stops inspiratory rhythm and impairs output in neonatal mice. eLife 3, e03427 (2014).
PubMed
PubMed Central
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Pagliardini, S., Greer, J. J., Funk, G. D. & Dickson, C. T. State-dependent modulation of breathing in urethane-anesthetized rats. J. Neurosci. 32, 11259–11270 (2012).
PubMed
Article
CAS
PubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
-
Saini, J. K. & Pagliardini, S. Breathing during sleep in the postnatal period of rats: the contribution of active expiration. Sleep https://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/zsx172 (2017).
-
Andrews, C. G. & Pagliardini, S. Expiratory activation of abdominal muscle is associated with improved respiratory stability and an increase in minute ventilation in REM epochs of adult rats. J. Appl. Physiol. 119, 968–974 (2015).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Rekling, J. C., Funk, G. D., Bayliss, D. A., Dong, X. W. & Feldman, J. L. Synaptic control of motoneuronal excitability. Physiol. Rev. 80, 767–852 (2000).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Burke, P. G. R. et al. State-dependent control of breathing by the retrotrapezoid nucleus. J. Physiol. 593, 2909–2926 (2015).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Boutin, R. C. T., Alsahafi, Z. & Pagliardini, S. Cholinergic modulation of the parafacial respiratory group. J. Physiol. 595, 1377–1392 (2016).
-
Mellen, N. M., Janczewski, W. A., Bocchiaro, C. M. & Feldman, J. L. Opioid-induced quantal slowing reveals dual networks for respiratory rhythm generation. Neuron 37, 821–826 (2003).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Janczewski, W. A. & Feldman, J. L. Distinct rhythm generators for inspiration and expiration in the juvenile rat. J. Physiol. 570, 407–420 (2006).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Huckstepp, R. T. R., Cardoza, K. P., Henderson, L. E. & Feldman, J. L. Role of parafacial nuclei in control of breathing in adult rats. J. Neurosci. 35, 1052–1067 (2015).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Huckstepp, R. T., Henderson, L. E., Cardoza, K. P. & Feldman, J. L. Interactions between respiratory oscillators in adult rats. eLife 5, e14203 (2016).
PubMed
PubMed Central
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Guyenet, P. G. & Bayliss, D. A. Neural control of breathing and CO2 homeostasis. Neuron 87, 946–961 (2015). This is a comprehensive review of chemosensation in the pF
V
(that is, the RTN).PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Guyenet, P. G. et al. Proton detection and breathing regulation by the retrotrapezoid nucleus. J. Physiol. 594, 1529–1551 (2016).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Feldman, J. L., Mitchell, G. S. & Nattie, E. E. Breathing: rhythmicity, plasticity, chemosensitivity. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 26, 239–266 (2003).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Gourine, A. V. et al. Astrocytes control breathing through pH-dependent release of ATP. Science 329, 571–575 (2010).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Wenker, I. C., Kréneisz, O., Nishiyama, A. & Mulkey, D. K. Astrocytes in the retrotrapezoid nucleus sense H+ by inhibition of a Kir4.1-Kir5.1-like current and may contribute to chemoreception by a purinergic mechanism. J. Neurophysiol. 104, 3042–3052 (2010).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Rose, M. F. et al. Math1 is essential for the development of hindbrain neurons critical for perinatal breathing. Neuron 64, 341–354 (2009).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Dubreuil, V. et al. Defective respiratory rhythmogenesis and loss of central chemosensitivity in Phox2b mutants targeting retrotrapezoid nucleus neurons. J. Neurosci. 29, 14836–14846 (2009).
PubMed
Article
CAS
PubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
-
Onimaru, H. & Homma, I. A novel functional neuron group for respiratory rhythm generation in the ventral medulla. J. Neurosci. 23, 1478–1486 (2003).
PubMed
Article
CAS
PubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
-
Onimaru, H., Ikeda, K. & Kawakami, K. CO2-sensitive preinspiratory neurons of the parafacial respiratory group express Phox2b in the neonatal rat. J. Neurosci. 28, 12845–12850 (2008).
PubMed
Article
CAS
PubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
-
Ruffault, P.-L. et al. The retrotrapezoid nucleus neurons expressing Atoh1 and Phox2b are essential for the respiratory response to CO2. eLife 4, e07051 (2015).
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Thoby-Brisson, M. et al. Genetic identification of an embryonic parafacial oscillator coupling to the preBötzinger complex. Nat. Neurosci. 12, 1028–1035 (2009).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Fortuna, M. G., West, G. H., Stornetta, R. L. & Guyenet, P. G. Bötzinger expiratory-augmenting neurons and the parafacial respiratory group. J. Neurosci. 28, 2506–2515 (2008).
PubMed
Article
CAS
PubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
-
Stornetta, R. L. et al. Expression of Phox2b by brainstem neurons involved in chemosensory integration in the adult rat. J. Neurosci. 26, 10305–10314 (2006).
PubMed
Article
CAS
PubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
-
Kang, B. J. et al. Central nervous system distribution of the transcription factor Phox2b in the adult rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 503, 627–641 (2007).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Abbott, S. B. G. et al. Selective optogenetic activation of rostral ventrolateral medullary catecholaminergic neurons produces cardiorespiratory stimulation in conscious mice. J. Neurosci. 33, 3164–3177 (2013).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Abbott, S. B. G., Stornetta, R. L., Coates, M. B. & Guyenet, P. G. Phox2b-expressing neurons of the parafacial region regulate breathing rate, inspiration, and expiration in conscious rats. J. Neurosci. 31, 16410–16422 (2011).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Holloway, B. B., Viar, K. E., Stornetta, R. L. & Guyenet, P. G. The retrotrapezoid nucleus stimulates breathing by releasing glutamate in adult conscious mice. Eur. J. Neurosci. 42, 2271–2282 (2015).
PubMed
PubMed Central
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Ikeda, K. et al. A Phox2b BAC transgenic rat line useful for understanding respiratory rhythm generator neural circuitry. PLOS ONE 10, e0132475 (2015).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Abbott, S. B. G. et al. Photostimulation of retrotrapezoid nucleus Phox2b-expressing neurons in vivo produces long-lasting activation of breathing in rats. J. Neurosci. 29, 5806–5819 (2009).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Bochorishvili, G., Stornetta, R. L., Coates, M. B. & Guyenet, P. G. Pre-Bötzinger complex receives glutamatergic innervation from galaninergic and other retrotrapezoid nucleus neurons. J. Comp. Neurol. 520, 1047–1061 (2012).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Rosin, D. L., Chang, D. A. & Guyenet, P. G. Afferent and efferent connections of the rat retrotrapezoid nucleus. J. Comp. Neurol. 499, 64–89 (2006).
PubMed
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Abdala, A. P. L., Rybak, I. A., Smith, J. C. & Paton, J. F. R. Abdominal expiratory activity in the rat brainstem–spinal cord in situ: patterns, origins and implications for respiratory rhythm generation. J. Physiol. 587, 3539–3559 (2009).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Moraes, D. J. A., Dias, M. B., Cavalcanti-Kwiatkoski, R., Machado, B. H. & Zoccal, D. B. Contribution of the retrotrapezoid nucleus/parafacial respiratory region to the expiratory-sympathetic coupling in response to peripheral chemoreflex in rats. J. Neurophysiol. 108, 882–890 (2012).
PubMed
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Marina, N. et al. Essential role of Phox2b-expressing ventrolateral brainstem neurons in the chemosensory control of inspiration and expiration. J. Neurosci. 30, 12466–12473 (2010).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Pagliardini, S. et al. Active expiration induced by excitation of ventral medulla in adult anesthetized rats. J. Neurosci. 31, 2895–2905 (2011). This report demonstrates active expiratory functions of the pF
L
.PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Shi, Y. et al. Neuromedin B expression defines the mouse retrotrapezoid nucleus. J. Neurosci. 37, 11744–11757 (2017).
PubMed
Article
PubMed Central
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Janczewski, W. A., Onimaru, H., Homma, I. & Feldman, J. L. Opioid-resistant respiratory pathway from the preinspiratory neurones to abdominal muscles: in vivo and in vitro study in the newborn rat. J. Physiol. 545, 1017–1026 (2002).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Silva, J. N., Tanabe, F. M., Moreira, T. S. & Takakura, A. C. Neuroanatomical and physiological evidence that the retrotrapezoid nucleus/parafacial region regulates expiration in adult rats. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 227, 9–22 (2016).
PubMed
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Takeda, S. et al. Opioid action on respiratory neuron activity of the isolated respiratory network in newborn rats. Anesthesiology 95, 740–749 (2001).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Sears, T. A., Berger, A. J. & Phillipson, E. A. Reciprocal tonic activation of inspiratory and expiratory motoneurones by chemical drives. Nature 299, 728–730 (1982).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Tuck, S. A., Dort, J. C. & Remmers, J. E. Braking of expiratory airflow in obese pigs during wakefulness and sleep. Respir. Physiol. 128, 241–245 (2001).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Dutschmann, M., Jones, S. E., Subramanian, H. H., Stanic, D. & Bautista, T. G. The physiological significance of postinspiration in respiratory control. Prog. Brain Res. 212, 113–130 (2014).
PubMed
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Pitts, T. et al. Coordination of cough and swallow: a meta-behavioral response to aspiration. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 189, 543–551 (2013).
PubMed
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Shannon, R. et al. Production of reflex cough by brainstem respiratory networks. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 17, 369–376 (2004).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Smith Hammond, C. A. et al. Predicting aspiration in patients with ischemic stroke: comparison of clinical signs and aerodynamic measures of voluntary cough. Chest 135, 769–777 (2009).
PubMed
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Bautista, T. G., Sun, Q.-J. & Pilowsky, P. M. The generation of pharyngeal phase of swallow and its coordination with breathing: interaction between the swallow and respiratory central pattern generators. Prog. Brain Res. 212, 253–275 (2014).
PubMed
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Wheeler Hegland, K., Huber, J. E., Pitts, T., Davenport, P. W. & Sapienza, C. M. Lung volume measured during sequential swallowing in healthy young adults. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 54, 777–786 (2011).
PubMed
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Jean, A. Brain stem control of swallowing: neuronal network and cellular mechanisms. Physiol. Rev. 81, 929–969 (2001).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Pitts, T. et al. Impact of expiratory muscle strength training on voluntary cough and swallow function in Parkinson disease. Chest 135, 1301–1308 (2009).
PubMed
PubMed Central
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Hernandez-Miranda, L. R. et al. Genetic identification of a hindbrain nucleus essential for innate vocalization. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 114, 8095–8100 (2017).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Richter, D. W. & Spyer, K. M. Studying rhythmogenesis of breathing: comparison of in vivo and in vitro models. Trends Neurosci. 24, 464–472 (2001).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Smith, J. C., Abdala, A. P. L., Borgmann, A., Rybak, I. A. & Paton, J. F. R. Brainstem respiratory networks: building blocks and microcircuits. Trends Neurosci. 36, 152–162 (2013).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Smith, J. C., Abdala, A. P. L., Koizumi, H., Rybak, I. A. & Paton, J. F. R. Spatial and functional architecture of the mammalian brain stem respiratory network: a hierarchy of three oscillatory mechanisms. J. Neurophysiol. 98, 3370–3387 (2007).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Richter, D. in Comprehensive Human Physiology: from Cellular Mechanisms to Integration (eds Greger, R. & Windhorst, U.) 2079–2095 (Springer, 1996).
-
Dutschmann, M. & Herbert, H. The Kölliker-Fuse nucleus gates the postinspiratory phase of the respiratory cycle to control inspiratory off-switch and upper airway resistance in rat. Eur. J. Neurosci. 24, 1071–1084 (2006).
PubMed
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Dutschmann, M. & Dick, T. E. Pontine mechanisms of respiratory control. Compr. Physiol. 2, 2443–2469 (2012).
PubMed
PubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
-
Poon, C.-S. & Song, G. Bidirectional plasticity of pontine pneumotaxic postinspiratory drive: implication for a pontomedullary respiratory central pattern generator. Prog. Brain Res 209, 235–254 (2014).
PubMed
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Anderson, T. M. et al. A novel excitatory network for the control of breathing. Nature 536, 76–80 (2016). This paper proposes that an autonomous postinspiratory oscillator circuit in the rostral medulla ordinarily couples with the preBötC during breathing to aid in inspiratory–expiratory phase transition.
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Ezure, K. & Tanaka, I. GABA, in some cases together with glycine, is used as the inhibitory transmitter by pump cells in the Hering-Breuer reflex pathway of the rat. Neuroscience 127, 409–417 (2004).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Ezure, K., Tanaka, I. & Kondo, M. Glycine is used as a transmitter by decrementing expiratory neurons of the ventrolateral medulla in the rat. J. Neurosci. 23, 8941–8948 (2003).
PubMed
Article
CAS
PubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
-
Tian, G. F., Peever, J. H. & Duffin, J. Mutual inhibition between Bötzinger-complex bulbospinal expiratory neurons detected with cross-correlation in the decerebrate rat. Exp. Brain Res. 125, 440–446 (1999).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Tian, G. F., Peever, J. H. & Duffin, J. Bötzinger-complex, bulbospinal expiratory neurones monosynaptically inhibit ventral-group respiratory neurones in the decerebrate rat. Exp. Brain Res. 124, 173–180 (1999).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Kam, K., Worrell, J. W., Janczewski, W. A., Cui, Y. & Feldman, J. L. Distinct inspiratory rhythm and pattern generating mechanisms in the preBötzinger complex. J. Neurosci. 33, 9235–9245 (2013). This paper presents the idea that burstlets, which are subthreshold for motor output, are nonetheless rhythmogenic in the preBötC.
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Stuart, D. G. & Hultborn, H. Thomas Graham Brown (1882–1965), Anders Lundberg (1920-), and the neural control of stepping. Brain Res. Rev. 59, 74–95 (2008).
PubMed
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Brown, T. G. On the nature of the fundamental activity of the nervous centres; together with an analysis of the conditioning of rhythmic activity in progression, and a theory of the evolution of function in the nervous system. J. Physiol. 48, 18–46 (1914).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
von Euler, C. On the central pattern generator for the basic breathing rhythmicity. J. Appl. Physiol. 55, 1647–1659 (1983).
Article
Google Scholar
-
Feldman, J. L. in Handbook of Physiology 463–524 (American Physiology Society, 1986).
-
Feldman, J. L. & Smith, J. C. Cellular mechanisms underlying modulation of breathing pattern in mammals. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 563, 114–130 (1989).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Zhang, W., Barnbrock, A., Gajic, S., Pfeiffer, A. & Ritter, B. Differential ontogeny of GABAB-receptor-mediated pre- and postsynaptic modulation of GABA and glycine transmission in respiratory rhythm-generating network in mouse. J. Physiol. 540, 435–446 (2002).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Brockhaus, J. & Ballanyi, K. Synaptic inhibition in the isolated respiratory network of neonatal rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 10, 3823–3839 (1998).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Funk, G. D. & Greer, J. J. The rhythmic, transverse medullary slice preparation in respiratory neurobiology: contributions and caveats. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 186, 236–253 (2013).
PubMed
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Richter, D. W. Generation and maintenance of the respiratory rhythm. J. Exp. Biol. 100, 93–107 (1982).
PubMed
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Richter, D. W. & Smith, J. C. Respiratory rhythm generation in vivo. Physiology 29, 58–71 (2014).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Dutschmann, M. & Paton, J. F. R. Glycinergic inhibition is essential for co-ordinating cranial and spinal respiratory motor outputs in the neonatal rat. J. Physiol. 543, 643–653 (2002).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Marchenko, V. et al. Perturbations of respiratory rhythm and pattern by disrupting synaptic inhibition within pre-Bötzinger and Bötzinger complexes. eNeuro https://doi.org/10.1523/eneuro.0011-16.2016 (2016).
-
Cregg, J. M., Chu, K. A., Dick, T. E., Landmesser, L. T. & Silver, J. Phasic inhibition as a mechanism for generation of rapid respiratory rhythms. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 114, 12815–12820 (2017).
PubMed
Article
PubMed Central
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Baertsch, N. A., Baertsch, H. C. & Ramirez, J. M. The interdependence of excitation and inhibition for the control of dynamic breathing rhythms. Nat. Commun. 9, 843 (2018).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Janczewski, W. A., Tashima, A., Hsu, P., Cui, Y. & Feldman, J. L. Role of inhibition in respiratory pattern generation. J. Neurosci. 33, 5454–5465 (2013). This paper demonstrates that blockade of inhibition in the preBötC and other sites in the medulla does not stop respiratory rhythm and breathing.
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Sherman, D., Worrell, J. W., Cui, Y. & Feldman, J. L. Optogenetic perturbation of preBötzinger complex inhibitory neurons modulates respiratory pattern. Nat. Neurosci. 18, 408–414 (2015).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Del Negro, C. A., Koshiya, N., Butera, R. J. Jr & Smith, J. C. Persistent sodium current, membrane properties and bursting behavior of pre-Bötzinger complex inspiratory neurons in vitro. J. Neurophysiol. 88, 2242–2250 (2002).
PubMed
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Del Negro, C. A. et al. Sodium and calcium current-mediated pacemaker neurons and respiratory rhythm generation. J. Neurosci. 25, 446–453 (2005).
PubMed
Article
CAS
PubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
-
Thoby-Brisson, M. & Ramirez, J. M. Identification of two types of inspiratory pacemaker neurons in the isolated respiratory neural network of mice. J. Neurophysiol. 86, 104–112 (2001).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Peña, F., Parkis, M. A., Tryba, A. K. & Ramirez, J.-M. Differential contribution of pacemaker properties to the generation of respiratory rhythms during normoxia and hypoxia. Neuron 43, 105–117 (2004).
PubMed
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Rekling, J. C. & Feldman, J. L. PreBötzinger complex and pacemaker neurons: hypothesized site and kernel for respiratory rhythm generation. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 60, 385–405 (1998).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Butera, R. J., Rinzel, J. & Smith, J. C. Models of respiratory rhythm generation in the pre-Bötzinger complex. I. Bursting pacemaker neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 82, 382–397 (1999).
PubMed
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Butera, R. J., Rinzel, J. & Smith, J. C. Models of respiratory rhythm generation in the pre-Bötzinger complex. II. Populations of coupled pacemaker neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 82, 398–415 (1999).
PubMed
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Del Negro, C. A., Johnson, S. M., Butera, R. J. & Smith, J. C. Models of respiratory rhythm generation in the pre-Bötzinger complex. III. Experimental tests of model predictions. J. Neurophysiol. 86, 59–74 (2001).
PubMed
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Koizumi, H. et al. Structural-functional properties of identified excitatory and inhibitory interneurons within pre-Bötzinger complex respiratory microcircuits. J. Neurosci. 33, 2994–3009 (2013).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Morgado-Valle, C., Baca, S. M. & Feldman, J. L. Glycinergic pacemaker neurons in preBötzinger Complex of neonatal mouse. J. Neurosci. 30, 3634–3639 (2010).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Doble, A. The pharmacology and mechanism of action of riluzole. Neurology 47, S233–241 (1996).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Guinamard, R., Simard, C. & Del Negro, C. Flufenamic acid as an ion channel modulator. Pharmacol. Ther. 138, 272–284 (2013).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Pace, R. W., Mackay, D. D., Feldman, J. L. & Del Negro, C. A. Role of persistent sodium current in mouse preBötzinger Complex neurons and respiratory rhythm generation. J. Physiol. 580, 485–496 (2007).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Paton, J. F. R., Abdala, A. P. L., Koizumi, H., Smith, J. C. & St-John, W. M. Respiratory rhythm generation during gasping depends on persistent sodium current. Nat. Neurosci. 9, 311–313 (2006).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Koizumi, H. & Smith, J. C. Persistent Na+ and K+-dominated leak currents contribute to respiratory rhythm generation in the pre-Bötzinger complex in vitro. J. Neurosci. 28, 1773–1785 (2008).
PubMed
Article
CAS
PubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
-
Chevalier, M., Toporikova, N., Simmers, J. & Thoby-Brisson, M. Development of pacemaker properties and rhythmogenic mechanisms in the mouse embryonic respiratory network. eLife 5, e16125 (2016).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Ramirez, J.-M., Tryba, A. K. & Peña, F. Pacemaker neurons and neuronal networks: an integrative view. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 14, 665–674 (2004).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Grillner, S. Biological pattern generation: the cellular and computational logic of networks in motion. Neuron 52, 751–766 (2006).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Grillner, S. The motor infrastructure: from ion channels to neuronal networks. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 4, 573–586 (2003).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Carroll, M. S. & Ramirez, J.-M. Cycle-by-cycle assembly of respiratory network activity is dynamic and stochastic. J. Neurophysiol. 109, 296–305 (2013).
PubMed
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Kam, K., Worrell, J. W., Ventalon, C., Emiliani, V. & Feldman, J. L. Emergence of population bursts from simultaneous activation of small subsets of preBötzinger Complex inspiratory neurons. J. Neurosci. 33, 3332–3338 (2013).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Feldman, J. L. & Del Negro, C. A. Looking for inspiration: new perspectives on respiratory rhythm. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 7, 232–242 (2006).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Feldman, J. L., Del Negro, C. A. & Gray, P. A. Understanding the rhythm of breathing: so near, yet so far. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 75, 423–452 (2013).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Feldman, J. L. & Kam, K. Facing the challenge of mammalian neural microcircuits: taking a few breaths may help. J. Physiol. 593, 3–23 (2015).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Kam, K. & Feldman, J. L. in Handbook of Brain Microcircuits 2nd edn 624 (Oxford Univ. Press, 2018).
-
Rekling, J. C., Champagnat, J. & Denavit-Saubié, M. Electroresponsive properties and membrane potential trajectories of three types of inspiratory neurons in the newborn mouse brain stem in vitro. J. Neurophysiol. 75, 795–810 (1996).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Rubin, J. E., Hayes, J. A., Mendenhall, J. L. & Del Negro, C. A. Calcium-activated nonspecific cation current and synaptic depression promote network-dependent burst oscillations. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 106, 2939–2944 (2009).
PubMed
PubMed Central
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Krey, R. A., Goodreau, A. M., Arnold, T. B. & Del Negro, C. A. Outward currents contributing to inspiratory burst termination in preBötzinger Complex neurons of neonatal mice studied in vitro. Front. Neural Circuits 4, 124 (2010).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Kottick, A. & Del Negro, C. A. Synaptic depression influences inspiratory-expiratory phase transition in Dbx1 interneurons of the preBötzinger complex in neonatal mice. J. Neurosci. 35, 11606–11611 (2015).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Mironov, S. L. Metabotropic glutamate receptors activate dendritic calcium waves and TRPM channels which drive rhythmic respiratory patterns in mice. J. Physiol. 586, 2277–2291 (2008).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Del Negro, C. A., Kam, K., Hayes, J. A. & Feldman, J. L. Asymmetric control of inspiratory and expiratory phases by excitability in the respiratory network of neonatal mice in vitro. J. Physiol. 587, 1217–1231 (2009).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Orlovskiı˘, G. N. Neuronal Control of Locomotion: from Mollusc to Man. (Oxford Univ. Press, 1999).
-
Lu, B. et al. The neuronal channel NALCN contributes resting sodium permeability and is required for normal respiratory rhythm. Cell 129, 371–383 (2007).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Lu, B. et al. Extracellular calcium controls background current and neuronal excitability via an UNC79-UNC80-NALCN cation channel complex. Neuron 68, 488–499 (2010).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Lu, B. et al. Peptide neurotransmitters activate a cation channel complex of NALCN and UNC-80. Nature 457, 741–744 (2009).
PubMed
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Yeh, S.-Y. et al. Respiratory network stability and modulatory response to substance P require Nalcn. Neuron 94, 294–303.e4 (2017).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Ono, T., Ishiwata, Y., Inaba, N., Kuroda, T. & Nakamura, Y. Hypoglossal premotor neurons with rhythmical inspiratory-related activity in the cat: localization and projection to the phrenic nucleus. Exp. Brain Res. 98, 1–12 (1994).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Dobbins, E. G. & Feldman, J. L. Differential innervation of protruder and retractor muscles of the tongue in rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 357, 376–394 (1995).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Ellenberger, H. H. & Feldman, J. L. Brainstem connections of the rostral ventral respiratory group of the rat. Brain Res. 513, 35–42 (1990).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Koizumi, H. et al. Functional imaging, spatial reconstruction, and biophysical analysis of a respiratory motor circuit isolated in vitro. J. Neurosci. 28, 2353–2365 (2008).
PubMed
Article
CAS
PubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
-
Stanek, E. 4th, Cheng, S., Takatoh, J., Han, B.-X. & Wang, F. Monosynaptic premotor circuit tracing reveals neural substrates for oro-motor coordination. eLife 3, e02511 (2014).
PubMed
PubMed Central
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Revill, A. L. et al. Dbx1 precursor cells are a source of inspiratory XII premotoneurons. eLife 4, e12301 (2015).
PubMed
PubMed Central
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Song, H. et al. Functional interactions between mammalian respiratory rhythmogenic and premotor circuitry. J. Neurosci. 36, 7223–7233 (2016).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Rekling, J. C., Shao, X. M. & Feldman, J. L. Electrical coupling and excitatory synaptic transmission between rhythmogenic respiratory neurons in the preBötzinger complex. J. Neurosci. 20, RC113 (2000).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Guerrier, C., Hayes, J. A., Fortin, G. & Holcman, D. Robust network oscillations during mammalian respiratory rhythm generation driven by synaptic dynamics. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 112, 9728–9733 (2015).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Hayes, J. A., Wang, X. & Del Negro, C. A. Cumulative lesioning of respiratory interneurons disrupts and precludes motor rhythms in vitro. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 109, 8286–8291 (2012).
PubMed
PubMed Central
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Pace, R. W., Mackay, D. D., Feldman, J. L. & Del Negro, C. A. Inspiratory bursts in the preBötzinger complex depend on a calcium-activated non-specific cation current linked to glutamate receptors in neonatal mice. J. Physiol. 582, 113–125 (2007).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Crowder, E. A. et al. Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate regulates inspiratory burst activity in the neonatal mouse preBötzinger complex. J. Physiol. 582, 1047–1058 (2007).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Morquette, P. et al. An astrocyte-dependent mechanism for neuronal rhythmogenesis. Nat. Neurosci. 18, 844–854 (2015).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Hülsmann, S., Oku, Y., Zhang, W. & Richter, D. W. Metabolic coupling between glia and neurons is necessary for maintaining respiratory activity in transverse medullary slices of neonatal mouse. Eur. J. Neurosci. 12, 856–862 (2000).
PubMed
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Huxtable, A. G. et al. Glia contribute to the purinergic modulation of inspiratory rhythm-generating networks. J. Neurosci. 30, 3947–3958 (2010).
PubMed
Article
CAS
PubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
-
Okada, Y. et al. Preinspiratory calcium rise in putative pre-Botzinger complex astrocytes. J. Physiol. 590, 4933–4944 (2012).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Angelova, P. R. et al. Functional oxygen sensitivity of astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 35, 10460–10473 (2015).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Rajani, V. et al. Release of ATP by pre-Bötzinger complex astrocytes contributes to the hypoxic ventilatory response via a Ca2+ -dependent P2Y1 receptor mechanism. J. Physiol. 589, 4583–4600 (2017).
-
Travers, J. B., DiNardo, L. A. & Karimnamazi, H. Medullary reticular formation activity during ingestion and rejection in the awake rat. Exp. Brain Res. 130, 78–92 (2000).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Welzl, H. & Bures, J. Lick-synchronized breathing in rats. Physiol. Behav. 18, 751–753 (1977).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Kleinfeld, D., Deschênes, M., Wang, F. & Moore, J. D. More than a rhythm of life: breathing as a binder of orofacial sensation. Nat. Neurosci. 17, 647–651 (2014).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Kurnikova, A., Moore, J. D., Liao, S.-M., Deschênes, M. & Kleinfeld, D. Coordination of orofacial motor actions into exploratory behavior by rat. Curr. Biol. 27, 688–696 (2017).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Nguyen Chi, V. et al. Hippocampal respiration-driven rhythm distinct from theta oscillations in awake mice. J. Neurosci. 36, 162–177 (2016).
PubMed
Article
CAS
PubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
-
Grion, N., Akrami, A., Zuo, Y., Stella, F. & Diamond, M. E. Coherence between rat sensorimotor system and hippocampus is enhanced during tactile discrimination. PLoS Biol. 14, e1002384 (2016).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Zelano, C. et al. Nasal respiration entrains human limbic oscillations and modulates cognitive function. J. Neurosci. 36, 12448–12467 (2016).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Li, P. et al. The peptidergic control circuit for sighing. Nature 530, 293–297 (2016). This report demonstrates that pF peptidergic neurons project to the preBötC to influence physiological sighing behaviour.
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Stornetta, R. L. Identification of neurotransmitters and co-localization of transmitters in brainstem respiratory neurons. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 164, 18–27 (2008).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Dubreuil, V. et al. A human mutation in Phox2b causes lack of CO2 chemosensitivity, fatal central apnea, and specific loss of parafacial neurons. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 105, 1067–1072 (2008).
PubMed
PubMed Central
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Li, P. & Yackle, K. Sighing. Curr. Biol. 27, R88–R89 (2017).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Lieske, S. P., Thoby-Brisson, M., Telgkamp, P. & Ramirez, J. M. Reconfiguration of the neural network controlling multiple breathing patterns: eupnea, sighs and gasps. Nat. Neurosci. 3, 600–607 (2000).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Ruangkittisakul, A. et al. Generation of eupnea and sighs by a spatiochemically organized inspiratory network. J. Neurosci. 28, 2447–2458 (2008).
PubMed
Article
CAS
PubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
-
Boiten, F. A., Frijda, N. H. & Wientjes, C. J. Emotions and respiratory patterns: review and critical analysis. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 17, 103–128 (1994).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Arch, J. J. & Craske, M. G. Mechanisms of mindfulness: emotion regulation following a focused breathing induction. Behav. Res. Ther. 44, 1849–1858 (2006).
PubMed
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Brown, R. P. & Gerbarg, P. L. Sudarshan Kriya Yogic breathing in the treatment of stress, anxiety, and depression. Part II — clinical applications and guidelines. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 11, 711–717 (2005).
PubMed
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Brown, R. P., Gerbarg, P. L. & Muench, F. Breathing practices for treatment of psychiatric and stress-related medical conditions. Psychiatr. Clin. North Am. 36, 121–140 (2013).
PubMed
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Descilo, T. et al. Effects of a yoga breath intervention alone and in combination with an exposure therapy for post-traumatic stress disorder and depression in survivors of the 2004 South-East Asia tsunami. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 121, 289–300 (2010).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Jella, S. A. & Shannahoff-Khalsa, D. S. The effects of unilateral forced nostril breathing on cognitive performance. Int. J. Neurosci. 73, 61–68 (1993).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Katzman, M. A. et al. A multicomponent yoga-based, breath intervention program as an adjunctive treatment in patients suffering from generalized anxiety disorder with or without comorbidities. Int. J. Yoga 5, 57–65 (2012).
PubMed
PubMed Central
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Paul, N. A., Stanton, S. J., Greeson, J. M., Smoski, M. J. & Wang, L. Psychological and neural mechanisms of trait mindfulness in reducing depression vulnerability. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 8, 56–64 (2013).
PubMed
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Zeidan, F., Johnson, S. K., Diamond, B. J., David, Z. & Goolkasian, P. Mindfulness meditation improves cognition: evidence of brief mental training. Conscious Cogn. 19, 597–605 (2010).
PubMed
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Carreno, F. R. & Frazer, A. Vagal nerve stimulation for treatment-resistant depression. Neurotherapeutics 14, 716–727 (2017).
PubMed
Article
PubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
-
Masaoka, Y., Izumizaki, M. & Homma, I. Where is the rhythm generator for emotional breathing? Prog. Brain Res. 209, 367–377 (2014).
PubMed
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Dayan, P. & Abbott, L. F. Theoretical Neuroscience: Computational and Mathematical Modeling of Neural Systems. (Massachusetts Institute of Technology Press, 2001).
-
Pathmanathan, P. & Gray, R. A. Verification of computational models of cardiac electro-physiology. Int. J. Num Method. Biomed. Eng. 30, 525–544 (2013).
Article
Google Scholar
-
Carroll, M. S., Viemari, J.-C. & Ramirez, J.-M. Patterns of inspiratory phase-dependent activity in the in vitro respiratory network. J. Neurophysiol. 109, 285–295 (2013).
PubMed
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Prinz, A. A., Bucher, D. & Marder, E. Similar network activity from disparate circuit parameters. Nat. Neurosci. 7, 1345–1352 (2004).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Alsahafi, Z., Dickson, C. T. & Pagliardini, S. Optogenetic excitation of preBötzinger complex neurons potently drives inspiratory activity in vivo. J. Physiol. 593, 3673–3692 (2015).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Del Negro, C. A., Morgado-Valle, C. & Feldman, J. L. Respiratory rhythm: an emergent network property? Neuron 34, 821–830 (2002).
PubMed
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Purvis, L. K., Smith, J. C., Koizumi, H. & Butera, R. J. Intrinsic bursters increase the robustness of rhythm generation in an excitatory network. J. Neurophysiol. 97, 1515–1526 (2007).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Smith, J. C. et al. Respiratory rhythm generation in neonatal and adult mammals: the hybrid pacemaker-network model. Respir. Physiol. 122, 131–147 (2000).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Song, H., Hayes, J. A., Vann, N. C., Drew LaMar, M. & Del Negro, C. A. Mechanisms leading to rhythm cessation in the respiratory preBötzinger complex due to piecewise cumulative neuronal deletions. eNeuro https://doi.org/10.1523/eneuro.0031-15.2015 (2015).
-
Schwab, D. J., Bruinsma, R. F., Feldman, J. L. & Levine, A. J. Rhythmogenic neuronal networks, emergent leaders, and k-cores. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlin. Soft Matter Phys. 82, 051911 (2010).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Webb, P. W. Synchrony of locomotion and ventilation in Cymatogaster aggregata. Can. J. Zool. 53, 904–907 (1975).
Article
Google Scholar
-
Wegner, N. C., Sepulveda, C. A., Aalbers, S. A. & Graham, J. B. Structural adaptations for ram ventilation: gill fusions in scombrids and billfishes. J. Morphol. 274, 108–120 (2013).
PubMed
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Wang, T., Carrier, D. R. & Hicks, J. W. Ventilation and gas exchange in lizards during treadmill exercise. J. Exp. Biol. 200, 2629–2639 (1997).
PubMed
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Bramble, D. M. & Carrier, D. R. Running and breathing in mammals. Science 219, 251–256 (1983).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Funk, G. D., Steeves, J. D. & Milsom, W. K. Coordination of wingbeat and respiration in birds. II. ‘Fictive’ flight. J. Appl. Physiol. 73, 1025–1033 (1992).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Perségol, L., Jordan, M., Viala, D. & Fernandez, C. Evidence for central entrainment of the medullary respiratory pattern by the locomotor pattern in the rabbit. Exp. Brain Res. 71, 153–162 (1988).
PubMed
ArticleGoogle Scholar
-
Funk, G. D., Milsom, W. K. & Steeves, J. D. Coordination of wingbeat and respiration in the Canada goose. I. Passive wing flapping. J. Appl. Physiol. 73, 1014–1024 (1992).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Funk, G. D., Valenzuela, I. I. & Milsom, W. K. Energetic consequences of coordinating wingbeat and respiratory rhythms in birds. J. Exp. Biol. 200, 915–920 (1997).
PubMed
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Potts, J. T., Rybak, I. A. & Paton, J. F. R. Respiratory rhythm entrainment by somatic afferent stimulation. J. Neurosci. 25, 1965–1978 (2005).
PubMed
Article
CAS
PubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
-
Lancaster, W. C., Henson, O. W. & Keating, A. W. Respiratory muscle activity in relation to vocalization in flying bats. J. Exp. Biol. 198, 175–191 (1995).
PubMed
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Speakman, J. R. & Racey, P. A. No cost of echolocation for bats in flight. Nature 350, 421–423 (1991).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Feldman, J. L. & McCrimmon, D. R. Fundamental Neuroscience 3rd edn (eds Squire, L. R. et al.) 855–872 (Academic Press, 2008).
-
Hayashi, F. & McCrimmon, D. R. Respiratory motor responses to cranial nerve afferent stimulation in rats. Am. J. Physiol. 271, R1054–R1062 (1996).
PubMed
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Jenkin, S. E. M., Milsom, W. K. & Zoccal, D. B. The Kölliker-Fuse nucleus acts as a timekeeper for late-expiratory abdominal activity. Neuroscience 348, 63–72 (2017).
PubMed
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
-
Pagliardini, S., Ren, J. & Greer, J. J. Ontogeny of the pre-Bötzinger complex in perinatal rats. J. Neurosci. 23, 9575–9584 (2003).
PubMed
Article
CAS
PubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
-
Thoby-Brisson, M., Trinh, J.-B., Champagnat, J. & Fortin, G. Emergence of the pre-Bötzinger respiratory rhythm generator in the mouse embryo. J. Neurosci. 25, 4307–4318 (2005).
PubMed
Article
CAS
PubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
-
Wallén-Mackenzie, A. et al. Vesicular glutamate transporter 2 is required for central respiratory rhythm generation but not for locomotor central pattern generation. J. Neurosci. 26, 12294–12307 (2006).
PubMed
Article
CAS
PubMed CentralGoogle Scholar
-
Gray, P. A. Transcription factors define the neuroanatomical organization of the medullary reticular formation. Front. Neuroanat. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnana.2013.00007 (2013).
PubMed
PubMed Central
Article
CASGoogle Scholar
